Guest post: Romania’s economic “Golden Age” - public perception versus the reality in numbers



In recent years, the collective perception of economic conditions and the future seems to be marked by increasing pessimism. Looking around us, we might think we are living in troubled times. Indeed, we have lived through global financial crises like the one in 2008, a pandemic, and other major events, but the impact of these events is often magnified.
The focus on negative news in the media and social media can fuel a sense of insecurity and fear about the present and the future. Moreover, human nature predisposes us to pay more attention to negative news, thus increasing the feeling of insecurity. The result is a distorted (as I will show below) but widespread perception that the "golden age" belongs to the past, while the present is dominated by instability and decline.
But economic indicators - objective barometers of the state of the economy - offer us a different perspective: the golden age is not to be found in the past, but rather in the present. In this sense, the graph below shows us that today, we are crossing an extraordinary, unprecedented chapter in Romania's economic history.
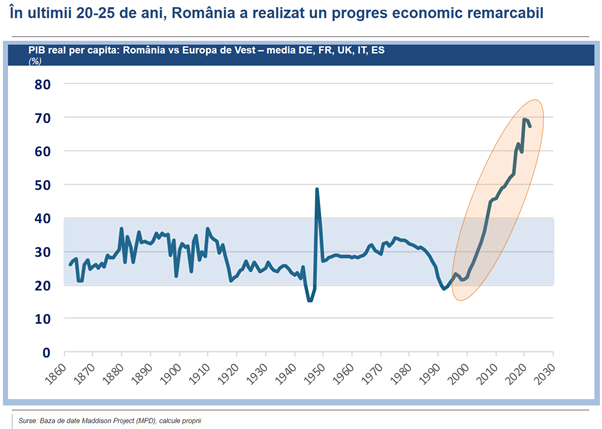
Analyzing the evolution of GDP per capita adjusted to purchasing power parity (a relevant benchmark for measuring economic progress and convergence) from 1862 to today, compared to the developed countries of Western Europe (Germany, France, Great Britain, Italy and Spain), we discover a surprising evolution, culminating in a remarkable performance in recent years.
This series of data, probably one of the most extensive of its kind, shows that Romania's level of development has fluctuated between 20% and 40% of the Western European average for about 140 years, maintaining an average of about 30 %. However, in the last two to three decades, Romania has registered accelerated economic growth, which can be considered a real "economic miracle,” propelling us towards a unique level of well-being in our entire history, with increased access to goods and services.
After almost a century and a half of underdevelopment, we have overcome the status of a low-income economy and advanced to a medium level of development. From a country deeply affected by the transition from a centralized to a market economy, we have become a complex economy, comparable to the economies of Central and Eastern European countries such as Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary, which are also in the range of 70-80% of the EU average in terms of GDP/ capita PPP. We are at a point where, despite internal and external challenges, we have made important progress, and economically and in terms of living standards, we are closer to the West than we have ever been.
A convergence as rapid as that experienced by Romania (and the Central and Eastern European region) in the last two and a half decades is rare. In Romania, the GDP per capita, in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP) compared to the EU average, increased spectacularly from approximately 25% to almost 80% during this period. Although regional disparities still persist in our country, overall progress is undeniable.
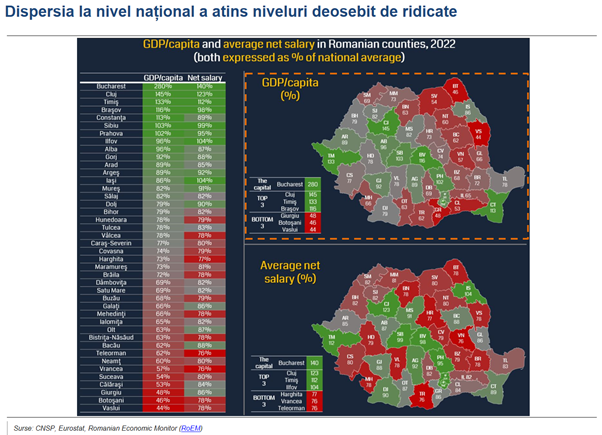
However, the overall picture of Romania's economic progress hides at least 42 nuances (the 41 counties plus the capital), reflecting notable geographical differences. Although the indicators at the national level show a clearly positive trend, regional inequalities and economic differences between counties create a much more complex and fragmented reality. Even in areas considered developed, there are social groups that have not benefited to the same extent from the process of economic convergence.
The economic differences between Romania's counties are obvious. The less-performing areas in terms of GDP per capita reach barely 44-48% of the national average, while top counties such as Brașov, Timiș, and Cluj reach values between 116% and 145%. Bucharest stands out, reaching 280% of the national average. Counties with higher economic performance are generally able to offer higher wages to employees, which increases inequality.
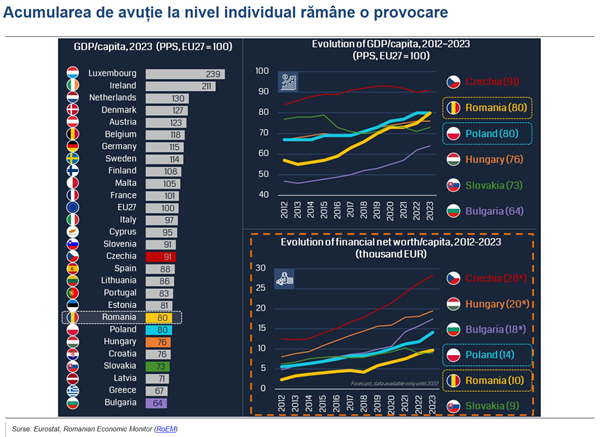
Although it is probably the most commonly used indicator to measure economic progress, GDP does not fully capture the true well-being of the population. If we look at stock indicators such as net financial wealth per capita, in contrast to flow indicators such as GDP per capita, we see a gap compared to our neighbors in Central and Eastern Europe. This suggests that while economic growth has been robust, wealth accumulation at the individual level remains a challenge.
Although the economic convergence is as clear as possible, the main question mark remains the sustainability of this positive trend. We have a long way to go until the well-being of each county and each social category in Romania approaches the level of those in the European Union. Reality is complex, with many nuances.
Furthermore, how we feel – our level of happiness and contentment – depends on a multitude of factors. GDP per capita is a simple indicator and cannot capture the complexity of human feelings. Moreover, certain cognitive biases can distort our perception of the past and present, such as " rosy retrospection ” (the tendency to idealize the past). Many tend to remember their youth or past times as better than they actually were.
But returning to the topic of convergence, the question naturally arises: how was this spectacular progress over the last 20-25 years possible? The short answer is: European integration.
The European project has a profound impact on our lives, promoting economic cooperation, raising living standards and supporting democracy, freedom and peace among member states. Membership of the European Union played an essential role in the convergence process of Central and Eastern European countries, including Romania. The accelerated development of this region in the last two decades is a case study, a rare example in economic history that highlights the advantages of European integration.
Integration into the European Union gave Romania access to a vast common market, structural funds, and unprecedented investment opportunities. The adoption of European standards, the implementation of structural reforms, and the strengthening of democratic institutions were key elements in this process.
This success formula can serve as an example for other countries that aspire to European integration, such as the Republic of Moldova. In the context of the recent elections in the Republic of Moldova, the European path is not only a geopolitical option but also a real opportunity for economic development and prosperity, even if this process is long-lasting and will require sustained efforts.
According to economic theory, growth is based on two fundamental elements: labor force contribution (number of employees and hours worked – L) and labor productivity (LP). The latter is determined by capital (equipment, factories, infrastructure – K) and total factor productivity (TFP), a measure of the efficiency of the use of economic resources, which reflects innovation, technological progress and the quality of management.
To illustrate this concept, imagine a worker from Central and Eastern Europe in a company in Western Europe or the United States. We often observe that it becomes as productive as its Western counterparts. On the other hand, if an employee in a highly developed country were to work in an environment with limited resources, his productivity would decline considerably. This emphasizes the key role that capital and technology play in increasing productivity.
European integration has allowed the Romanian workforce to become approximately three times more productive today compared to the beginning of this century, unlocking huge growth potential.
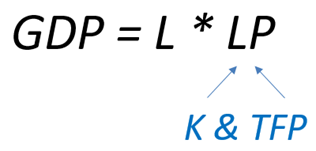
Romania's transformation from a closed economy to an open market economy has made it possible for us to participate in international trade and integrate into global value chains. This path has brought challenges and intense competition, but the positive impact on the economy is undeniable.
In addition, European funds have supported essential reforms and investments in infrastructure and public services, contributing directly to economic growth. Foreign direct investment (FDI) has also played a decisive role, providing capital and increasing total factor productivity through the transfer of technology and managerial expertise, indispensable elements of a modern economy.
Last but not least, strong institutions have played a key role in this transformation, as argued by the 2024 Nobel Prize laureates in Economics, Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson, and James Robinson, in their studies of how institutions influence the prosperity of nations. We adopted models, legislative frameworks, and knowledge systems developed and successfully tested in Western Europe, which contributed to increasing Romania's economic stability and competitiveness.
In the last quarter of a century, Romania reached an average rate of convergence with the EU average of approximately 2 percentage points per year, but with the approach to the European level, the road becomes increasingly difficult. The pace of convergence is expected to slow in the coming years, both because of the complexity of the next steps and the specific challenges looming on the horizon. The threat of the "middle-income trap" appears, specific to developing countries that have difficulty taking the next step and becoming developed economies.
The first limiting factor is the proximity to the technological frontier. If the jump from 25% to 75% of the EU average was challenging but achievable, the increase from 75% to 100% requires constant innovation and massive investment in technology. A relevant analogy would be driving a car in fog on a winding mountain road. Initially, we follow the lights of the car in front (Western models), but once we pass it, we realize that we no longer have a clear guide and must discover our own direction. At the technological frontier, progress depends on our ability to innovate and adapt.
The labor market represents another challenge on the road to full convergence. If in the 2000s Romania had a high unemployment rate and a relatively cheap workforce, today the situation has changed. In the context of a reduced natural increase and the problem of emigration, access to highly qualified labor is becoming increasingly difficult.
Fiscal policy also becomes a limiting factor. Given that larger, unsustainable deficits have been tolerated in recent years, we see that public debt has grown rapidly, from around 12% of GDP in 2007 to almost 52% in 2024. Prudent management of public finances and gradual fiscal consolidation are essential for maintaining economic stability.
European funds will continue to play an important role, but their contribution may diminish in the medium term. As we approach the standard of living of the more developed states in the EU, financial resources will have to be directed to other priorities of the Union. The EU itself faces major challenges, such as the need to improve economic competitiveness (as the Draghi report points out) alongside other strategic initiatives (e.g., defense), supporting other states pursuing the integration or reconstruction of Ukraine.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is another element but with mixed prospects. On the one hand, the tense geopolitical context can discourage investors, who become more cautious in their decisions. On the other hand, the trends of near-shoring and friend-shoring – relocating production closer to the markets or in friendly countries – can create opportunities for Romania if we manage to attract these investments through appropriate policies.
In order to continue the convergence process, Romania must develop internal engines of economic growth. A possible catalyst (country project) could be joining the Eurozone. The preparation process and reforms required for the adoption of the euro can stimulate the modernization of the economy and strengthen investor confidence. The road to the euro area is as important as the actual adoption of the single currency.
With realistic optimism, it can be said that by the end of this decade, Romania could reach 85-90% of the EU development average.
So when was or is the "golden age"? There are objective arguments to suggest that we are in a special time economically, with remarkable progress and unique opportunities. However, as one experienced former central banker said, just like in a relationship, the golden age in economics is often only seen when things stop working.
Personally, I would like to believe that our true economic golden age is just ahead, waiting to be built by our efforts and aspirations. In a global context marked by immense challenges, Romania has a real chance to continue its progress. But this chance requires work, vision and commitment, and the first test awaits us next year itself, when we will be faced with the need to gradually reduce macroeconomic vulnerabilities, especially the budget deficit.
About the author
Csaba Bálint is a Board member of the National Bank of Romania. Before joining NBR in 2019, he worked at a universal bank in different positions. Between 2008 and 2014, he was in the institution’s Risk Division, being responsible for macroeconomic stress testing and credit scorecard developments. At the end of 2014, he moved to the Finance and Planning Division as macroeconomic analyst, preparing analysis and forecasts about the Romanian economy, financial markets and banking system. He also teaches at universities in Cluj-Napoca and Oradea. Csaba passed the level III CFA exam in 2016 and holds M.Sc. in finance from the Bucharest University of Economic Studies.
This opinion article was translated from the blog opiniibnr.ro and represents the author's views and not those of the BNR.
---
*This is an opinion article and the views expressed here belong to the author. If you want to participate in the debate and share your views on political and social topics, or on things related to life in Romania in general, please write to us at newsroom@romania-insider.com.
(Opening photo source: ID 256478797 | Business © Vitalii Petrushenko | Dreamstime.com)